
Crop focus
Going bananas
It’s the world’s most popular fruit: every year, the 100 billion bananas we chomp our way through account for more than three-quarters of the tropical fruit trade. But as news of the first genetically modified banana has recently revealed, it’s a precarious trade.
Nearly every banana sold in every shop, in every country, on every continent, is a clone. They’re all examples of the Cavendish banana. Its ubiquity came about in the 1950s and 1960s because the previous global favourite – the Gros Michel – succumbed to the devastating Panama disease, caused by a form of Fusarium known as Tropical Race 1 (TR1).
The Gros Michel banana was itself a genetic clone, lacking the diversity that might have allowed it to evolve a genetic defence against attack by TR1. Instead, the Cavendish – a higher yielding variety, with thicker skin that made it even better suited to export – was selected from a naturally occurring hybrid that displayed the necessary resistance to TR1. It quickly became the world’s dominant banana variety, grown everywhere from South America to Africa and throughout Asia and into Australia.
But in 1990, a new disease – TR4 – was detected in Taiwan. Now widespread in more than 20 banana-producing countries, according to the FAO, it has put the Cavendish in potentially the same precarious position as the Gros Michel, eighty years ago. We could be facing a banana crisis on a global scale: in an industry worth $25bn, with annual production of more than 125 million tonnes, that’s a chilling thought.
What’s so devastating about Panama disease? Effectively, the total death of the plant: yellowing leaves quickly brown, before falling off. Then the fungus moves into the stem and roots, killing the tissue as it moves throughout the plant. Even replanting is not the solution. Once in the soil, TR4 becomes virtually impossible to eradicate.
It’s for this reason that the Australian government has approved an application from Queensland University of Technology to release QCAV-4, a genetically modified Cavendish variety developed to show resistance to TR4.
The resistance gene, labelled RGA2, has been taken from a wild banana variety found in South-East Asia. Interestingly, the gene is already present, although dormant, in the Cavendish variety. Approval of the variety gives the researchers the go-ahead to trial it in real conditions on farm; there are no plans yet to allow consumers to buy the new GM banana.
They’ll also try to use the CRISPR technique – gene-editing – to introduce the resistant gene, as gene-editing poses fewer hurdles when it comes to acceptance by regulators and consumers.
Another disease the researchers have identified as a target for gene-edited varieties is black sigatoka, brought on by the fungus Mycosphaerella fijiensis. A foliar disease that causes lesions, chlorosis and physical collapse of the leaf, black sigatoka will ultimately cause the death of the plant. Chemical control is possible but requires an intense spraying programme of up to 50 applications every year. Even then, yield may be slashed by as much as 50%.
Adding to this grim outlook is the loss of many of the active ingredients that are most effective against black sigatoka. Mancozeb, for example, has already been banned in many countries; growers still permitted to apply it may nonetheless be prevented from using it, owing to production protocols imposed by their buyers.
But with any genetic solution still some way off, what’s the best option for banana producers facing the headache of black sigatoka? It’s a challenge that FertiGlobal took up.
Finding and commercialising these breakthrough solutions, that can assure farmers of yield and quality while observing regulatory parameters and environmental obligations, are FertiGlobal’s ‘bread and butter’. To help farmers navigate the threat of black sigatoka, we turned to our EnNuVi Technology, the patented nutrient-polyphenolic-molecule that focuses on facilitating the strengthening of the plant’s natural defence systems.
There’s a wealth of evidence to show that a balanced combination of nutrients – putting the plant in good stead – fortifies the plant, reducing its susceptibility to both biotic and abiotic stresses. With better health comes increased energy, allowing it to use its own in-built mechanisms to ward off attack by pathogens such as Mycosphaerella. If a plant can resist infection, a farmer’s need for fungicides is much reduced.
FertiGlobal took EnNuVi technology to India and the Philippines – respectively the world’s largest and sixth-largest banana producers – for trials.
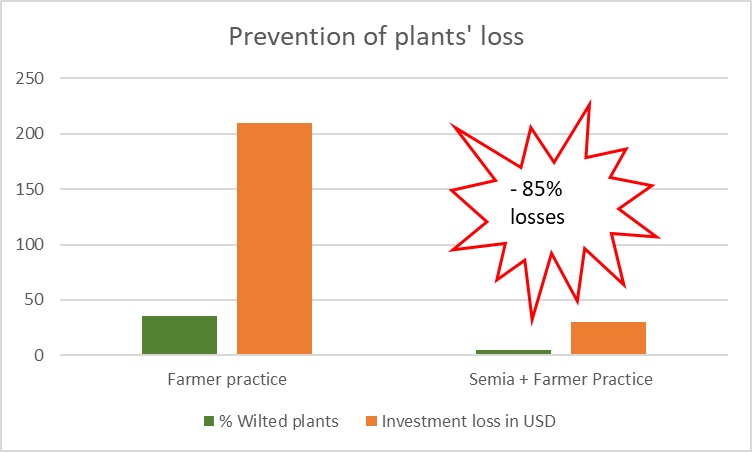
The first trial, conducted in India, examined the losses induced in banana plants through leaf wilting. Farmer standard practice often saw wilting in more than half of all plants, leading to a loss in crop ROI of over $200/ha. But in plants treated with the EnNuVi-enabled Semia, the percentage of wilting plants was slashed to less than 10%, reducing investment loss by 85%.
Meanwhile, in the Philippines, the trial proposed to see whether EnNuVi would increase the number of functional leaves on each banana plant, boosting overall plant health and energy levels to help it fight stress and attack. Of all the EnNuVi products tested, Mantus provided the best result: a 44% increase in functional leaves, over the standard practice, after 45 days.
So while EnNuVi products can’t be seen as a direct replacement for mancozeb, because they don’t exhibit any fungicidal properties, they can – if applied at the correct time in the crop cycle – provide growers with an earlier alternative that may alleviate their need for fungicides at a later date.
We’re not stopping at bananas, of course. FertiGlobal is committed to ensuring continuing success in every crop in which we have an interest. If we can help farmers, wherever they are in the world, reduce the use of agrochemicals and maintain or increase their crop’s productivity and yield, we’ll find a way to do it. It’s the FertiGlobal way.

